✔ 100% Authentic Product
👁️ Currently Viewing 2357
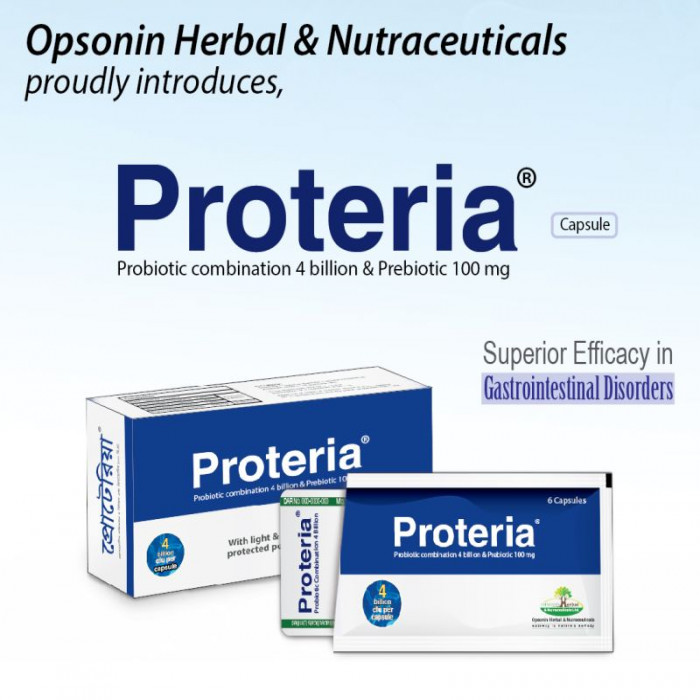
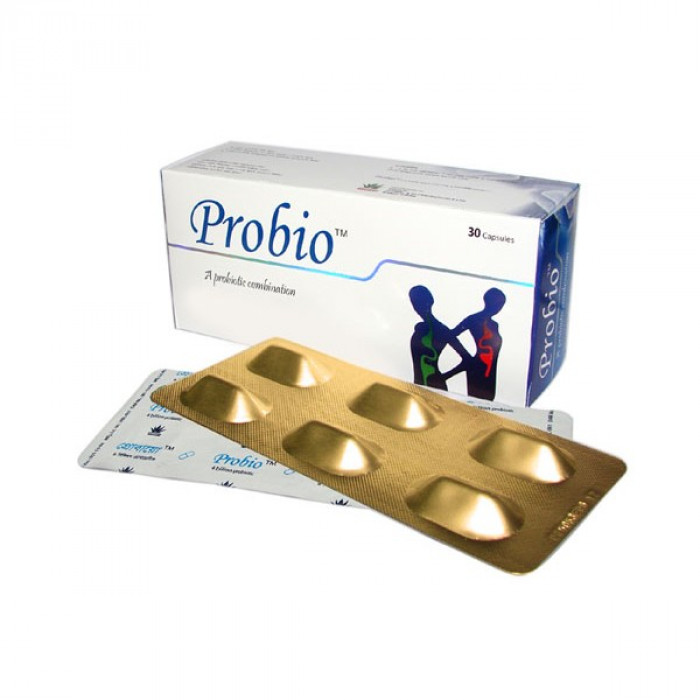
Probio Capsule
Probiotic Combination 4 Billion formulations are rich in beneficial live bacteria. It generates spores during its reproductive life cycle which makes it robust unlike other probiotics and withstands extreme environments. Probio Capsule is very useful for the digestive system.

100% Genuine Products, Guaranteed
Safe & Secure Payments, Always
Fast, Secure & Efficient Delivery
Proper Packaging
 Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh
Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City*
Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, All Over Bangladesh*
Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, All Over Bangladesh* ফ্রি ডেলিভারি! - ১৪৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে ঢাকা
শহরে ।
ফ্রি ডেলিভারি! - ১৪৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে ঢাকা
শহরে ।
✅ Description:
Probio Capsule is a Dietary Supplement formulated with probiotics and prebiotics to support your digestive health. Probiotics support healthy digestion, nutrient absorption, and immune function. It may help prevent the growth of harmful bacteria in the gut. It may also help relieve occasional gas, constipation, and irritable bowel syndrome.
✔️ Uses of Probio Capsule
- Dietary Supplement
✔️ Composition
Each capsule contains-
- Lactobacillus acidophilus (2 billion)
- Lactobacillus bulgaricus (1 billion)
- Bifidobacterium bifidum (1 billion) is a 4 billion probiotic combination and
- Fructo-oligosaccharides (100 mg)
✔️ How does Probio Capsule work?
Probiotics have been shown to reduce experimental and human gastrointestinal inflammation (human inflammatory bowel disease) through their effects on epithelial cell function, including epithelial cell barrier function, epithelial cytokine secretion, and antibacterial effects related to epithelial layer colonization in recent studies.
✔️ Side Effects of Probio Capsule
There are no known toxicities or side effects.
✔️ Key Benefits:
- Helpful in irritable bowel syndrome
- Aids in healing diarrhoeal conditions
- Enhances immunity and is useful for the digestive system
- It may repopulate the good intestinal bacteria
✔️ Indications of Probio Capsule
This can be seen in the following examples:
- Diarrhea
- Anxiety in the stomach
- Lactose intolerance is a condition in which a person is unable to digest
- Infection of the vaginal canal
- Diarrhea caused by antibiotics
✔️ Pharmacology
Probiotics are living microorganisms, such as Lactobacillus species, Bifidobacterium species, and yeasts, that can have a beneficial impact on the host when consumed by improving the balance of the intestinal microflora. These microorganisms are naturally present in various foods, including dairy, grains, meat, and fish, and even in the human and animal intestines, mouths, and vaginas.
Lactobacillus acidophilus is a specific bacteria belonging to the Lactobacillus genus. Its name derives from "lacto" (referring to milk), "bacillus" (rod-like shape), and "acidophilus" (acid-loving). L. acidophilus occurs naturally in a variety of foods and is commonly found in the human and animal intestines, mouths, and vaginas. These types of beneficial bacteria help maintain a healthy balance by protecting against harmful organisms.
Lactobacillus bulgaricus, on the other hand, is one of the bacteria used in the production of yogurt. It was first identified by Bulgarian doctor Stamen Grigorov in 1905 and is named after Bulgaria. L. bulgaricus is a gram-positive rod-shaped bacterium that does not have motility or spore-forming ability. It thrives on milk and produces lactic acid, which contributes to the preservation of milk. This bacterium also helps break down lactose, making it beneficial for individuals with lactose intolerance. Additionally, during the fermentation of milk, L. bulgaricus produces acetaldehyde, which gives yogurt its characteristic aroma.
Bifidobacteria are naturally found in the human and animal colon. They are particularly abundant in newborns, especially those who are breastfed. Bifidobacteria were first isolated from the feces of breast-fed infants. These gram-positive anaerobic bacteria are non-motile, do not form spores, and are catalase-negative. They are named "bifidobacteria" because they often appear in a "Y"-shaped or bifid form. Currently, around 30 species of bifidobacteria have been identified.
Overall, these different species of bacteria play important roles in maintaining a healthy gut microbiota, and their consumption as probiotics has been associated with various health benefits.
✔️ Dosage & Administration of Probio Capsule
- Take one Natures Velvet Lifecare Probiotic Capsule daily before meals
- Use as directed on the label or as directed by your physician
- Do not exceed the recommended dose
✔️ Interaction
None of them are well-documented.
✔️ Contraindications
The use of probiotics may not be advised in certain situations, including patients at risk of opportunistic infections and those with severely damaged gastrointestinal tracts. Here are some important considerations:
Patients at risk of opportunistic infections: Individuals with compromised immune systems, such as those undergoing immunosuppressive therapy or with HIV/AIDS, may be at increased risk of developing opportunistic infections. Probiotics, particularly those containing live bacteria, may pose a potential risk in these individuals, as the introduction of additional microorganisms could lead to infection. It is crucial for such patients to consult with their healthcare provider before using probiotics.
Severely damaged gastrointestinal tracts: In cases where the gastrointestinal tract is severely damaged, such as in patients with acute pancreatitis, perforated bowel, or other serious gastrointestinal conditions, the use of probiotics may not be recommended. The introduction of live microorganisms in these situations could potentially worsen the condition or lead to infections. Healthcare professionals should evaluate the specific circumstances and determine the appropriateness of probiotic use on a case-by-case basis.
✔️ Pregnancy & Lactation
Probiotics are unlikely to reach the systemic circulation of the fetus & therefore are unlikely to cause harm. Probiotics are unlikely to be transferred into breast milk.
✔️ Precautions & Warnings
Probiotics, herbal and nutraceuticals
✔️ Storage Conditions
Store below 25ºC, in a dry place, and away from direct sunlight. Keep out of reach of children.
⚠️Disclaimer:
At ePharma, we’re committed to providing accurate and accessible health information. However, all content is intended for informational purposes only and should not replace medical advice from a qualified physician. Please consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance. We aim to support, not substitute, the doctor-patient relationship.